Study Destinations - Australia

Australia
- About Australia
- Why Australia
- Interesting facts about Australia
- Australian Education system
- Student visa process
About Australia
Australia is a stable, democratic and culturally diverse nation with a highly skilled workforce and one of the strongest performing economies in the world.With spectacular landscapes and a rich ancient culture, Australia is a land like no other. It is the earth’s sixth-largest country in land area and is the only nation to govern an entire continent. The climate ranges from wet tropics to the Arid outback with just about everything in between. Equally famous for it’s landscapes of pristine beaches, tropical islands and the rugged outback as it is for it’s cities, each with a unique personality and culture. Exploring Australia should be a must on everyone’s travel wishlist.
Australia is divided politically into six States and two Territories.
Australian Capital Territory (ACT) – Canberra
Canberra is Australia’s federal capital and the largest inland city. Set in a broad valley in the southern tablelands of New South Wales, Canberra is a well-planned lakeside city of parklands, impressive restaurants, beautiful bushland and leafy suburbs.
Canberra is only a three-hour drive or a 45-minute flight south-west of Sydney. It also has many national attractions, embassies and public buildings.
Canberra is famous for:
New South Wales (NSW) – Sydney
New South Wales was founded in 1788 and is Australia’s oldest State. A narrow coastal plain runs the length of its east coast, and to the west is the Great Dividing Range. Beyond these mountains, a tableland gradually slopes down to the plains, which cover most of the State.
NSW is the most populous State in Australia and the majority of its inhabitants live along the coast. It has dense forests, alpine country, deserts, and golden-sand beaches and bays on its North Coast.
Australia’s longest river system, the Murray-Darling, is situated in this State. Agriculturally, it is renowned for its sheep and beef industry.
NSW is famous for:
- The Sydney Opera House.
- The Sydney Harbour Bridge.
- The Blue Mountains – a national park about 1 hour west of Sydney.
Queensland (Qld) – Brisbane
Queensland takes up about one-fifth of the area of Australia. Along its eastern coastline are fertile plains and river valleys, which sometimes extend up to 200 km inland. The Great Dividing Range borders these lowlands, stretching south from Cape York to the New South Wales border. The major agricultural products are tropical fruits, beef and wool.
Brisbane was settled by convicts in 1825 and with its sunny days and tropical weather, is now the fastest growing city. Just north of Brisbane are the beaches and coastal lakes of the Sunshine Coast, and to the south is the popular tourist destination of the Gold Coast.
Queensland is famous for:
- The rainforests of Far North Queensland.
- The Great Barrier Reef – a more than 2000 km long coral reef north-east of the mainland.
- Fraser Island – the largest sand island in the world, which is 3 hours north of Brisbane.
- The Gold Coast – a major holiday destination for national and international tourists.
South Australia (SA) – Adelaide
South Australia is the driest state in Australia. Over 60% of it is desert and 80% receives less that 250mm of rain per year. However, the south-east corner has dry warm summers and cool wet winters. Along with rich fertile soil, this climate makes it ideal for growing wine.
Adelaide contains some of Australia’s best-preserved Victorian architecture. This gracious city is surrounded by parkland and is home to 73% of South Australians.
SA is famous for
- The Barossa Valley – a major wine producing area north-east of Adelaide.
- Coober Pedy – an opal mining town that is underground.
- The Adelaide Festival of Arts – held every 2 years.
Tasmania (Tas) – Hobart
Tasmania was cut off from mainland Australia at the end of the last Ice Age, and it is known for its unique wildlife, wilderness and unspoiled beauty. The National Parks offer one of the last great wilderness areas in the world. Tasmania’s capital Hobart, was settled in 1803 when the British government in Sydney sent soldiers and convicts there to protect their sealing and whaling interests.
Tasmania has substantial farming, forestry, hydro-electric, mining and fishery industries.
Tasmania is famous for:
- Port Arthur Historic site – this once was a prison for convicts.
- The Sydney to Hobart yacht race – starts every year on Dec 26th.
- Its bushwalking – many wilderness areas are only accessible on foot.
Victoria (Vic) – Melbourne
Victoria is the smallest state on Australia’s mainland. It was settled in 1834 and separated from New South Wales in 1851 at the time when gold was discovered at Ballarat and Bendigo.
Its capital, Melbourne offers colonial and contemporary architecture, beautiful botanical gardens, excellent restaurants and a vibrant artistic community. Melbourne is also considered Australia’s sporting capital and holds the most famous horse race in Australia each November: the Melbourne Cup. Victoria’s High Country offers some of the best mountain climbing on the continent.
Victoria is famous for:
- The goldfields of central Victoria.
- Sporting events such as the Melbourne Cup horse race.
- The Great Ocean Road – spectacular coastal scenery west of Melbourne.
Western Australia (WA) – Perth
Western Australia is the largest state in Australia. The capital, Perth is situated on the Swan River and has all the modern conveniences, while maintaining a friendly and relaxed feeling. White sandy beaches are only minutes from the city.
Rich farmland lies inland as well as some of the world’s most productive goldfields. The state’s wealth also includes iron, nickel, wheat and wool, which are mostly exported from the port of Fremantle.
The north of the state boasts a wide variety of attractions including gorges and national parks, the stunning beaches of Broome, and the friendly dolphins of Monkey Mia.
WA is famous for:
- Kalgoorlie – a gold mining town located in the Western Desert.
- Ningaloo Marine Park – 1,200 km north of Perth.
- Fremantle (20mins south-west of Perth).
Why Australia
An academic degree from an Australian university is held in high regard throughout the world. Australia offers best courses in some of the most popular disciplines like Health, Engineering & Technology, Social Sciences, Arts & Humanities and Physical Sciences. It is statistically the number one destination for international students, beating USA, UK and Canada. The culturally vibrant academic scene makes it an ideal destination from students all over the world. Not only do you study your course, you actually learn by doing. A safe, enjoyable lifestyle and pristine nature is another reason to choose Australia for your international degree.
Interesting facts about Australia
Australia performs very well in many measures of well-being relative to most other countries in the Better Life Index. Australia ranks at the top in civic engagement and above the average in income and wealth, environmental quality, health status, housing, jobs and earnings, education and skills, subjective well-being, and social connections
- Around 72% of people aged 15 to 64 in Australia have a paid job,
- 80% of adults aged 25-64 have completed upper secondary education
- The average student scored 502 in reading literacy, maths and science in the OECD’s Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA).
- In terms of health, life expectancy at birth in Australia is around 83 years
- 5 Australian cities are among the Top 30 Best Cities in the World for students
- 7 Australian Universities are among the Top 100 Universities in the World
- Australian University Ranking System is ranked 8th in the world, ahead of Japan, UK, Germany and Netherlands
- Australia performed better that the USA or UK in all areas.
- Australia was among the top ten countries in all three areas.
- The top 5% of Australian students achieved at the same level in all domains as the top 5% of students in any country
Australian Education System
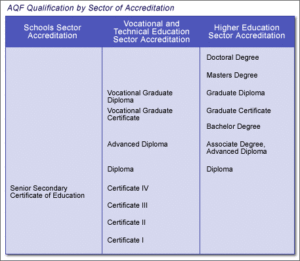
The Australian Qualifications Framework (AQF)
The Australian Qualifications Framework (AQF) is a system of seventeen national qualifications in 3 sectors:
- Schools,
- Vocational Education and Training (TAFE and private providers),
- Higher Education (mainly universities).
- The qualifications shown below are grouped according to the educational sector in which they are most commonly issued.
VET
Australia’s Vocational Education and Training (VET) sector offers a large variety of qualifications for students with a strong practical orientation. According to AEI, in 2013 there were 98,792 international student enrolments in VET courses in Australia. The top three source countries were India, Korea and Thailand.
The Institutions
The Australian VET system is publicly and privately funded and is delivered by a wide variety of training institutions and enterprises.
TAFE – Technical and Further Education
More than 60 TAFE institutes deliver VET training across Australia. They are government funded, they provide post-school education and training, and they usually have a more practical focus than university courses.
TAFE colleges act independently of one another and have their own premises, courses, and academic and administrative staff.
TAFEs can be very large institutions and have more students enrolled than many Universities. For example, most city-based TAFEs have over 50,000 enrolments. The facilities available to students are similar to those in a University. Also, they operate across a number of campuses as well as in industry and community venues.
TAFE institutes contain some of the largest ELICOS centres in Australia. They are also sometimes part of a University. For example, every university in Victoria except one has a TAFE division.
TAFE courses are often used by international students as a pathway to undergraduate programs at university, especially via the Diploma route. Some TAFEs offer university degrees through affiliated universities, and some offer their own degrees.
Private Colleges
There are approximately 5000 other registered providers of VET courses. These range from small institutions that offer specialised courses in one particular area of study to large private colleges which are similar to larger TAFE institutes.
A wide variety of VET courses are offered through private colleges. The most popular courses for international students are those related to Business and Information Technology.
Like TAFE, private colleges are popular with international students as pathway institutions, since they can provide entry to university studies after completing a VET qualification. Also, some private institutions offer university programs through affiliated universities, and others offer their own degrees.
Universities
There are 41 Australian universities, of which 3 are private (Bond, Torrens and Notre Dame). In addition, Carnegie Mellon and University College London have campuses in Adelaide, South Australia. As the main campuses and administrations of these university are established in Pennsylvania, USA and London UK respectively; we consider them as non-Australian universities.
Many Australian universities have overseas branch campuses, twinning arrangements and exchange programs for students and teaching staff worldwide. Australian universities have around 7000 agreements with universities (and similar institutions around the world).
Australian Universities have three primary roles:
- Storing knowledge;
- Transferring knowledge to others;
- Creating knowledge.
In addition to this, Australian Universities provide consultancy services to business and industry, and are a source of advice for Government and the community in general on a large number of issues and topics. They are closely involved with their local and wider communities.
Diversity and autonomy are central features of Australian universities. Each institution has the freedom to specify its own mission and purpose, modes of teaching and research, the makeup of their student body, and the range and content of their educational programs. This variety is reflected in the range of goals and objectives, staff profiles and the emphasis placed on particular courses at different universities.
As an agent, you need to be aware of the particular goals of the universities that you promote.
Higher education in Australia enjoys a high international reputation. Australian universities are part of a clearly recognized international community of scholarship, with academic staff recruited internationally, and students also increasingly coming from overseas as well as from across Australia. At the same time there are increasing numbers of Australian students and staff on study and work exchanges overseas.
- Student application process
STEP 1: ATTEND A COUNSELING SESSION
Attend a counseling session to find out your options relating to study destination, courses available and institutions.
STEP 2: APPLY FOR OFFER LETTER
Once you have decided what and where you want to study, we will help you to complete the application to the institutions of your choice. At the time of application for admission you will be required to submit several documents including proof of previous academic qualifications, proof of your English language ability, Work experience related documents and copy of passport. Average processing time to obtain admission letter is between 1 to 7 working days depending on institution and course.
Note-Depending on institute policy you may need to show funds equivalent to tuition fee and living expenses to institutions. Some institutes may conduct interview as well. Thereafter student need to pay their fee for the course to get the admission letter.
STEP 3: PAY TUITION FEES
To accept your offer from an education provider, you must pay the tuition fee. Most Australian institutions require you to pay the first semester fee only. You can choose to pay this fee through either Telegraphic Transfer (TT) or Direct Debit (DD). Once the institutions have received and processed your tuition fee payment, they will issue you with an Electronic Confirmation of Enrolment (ECoE). Average processing time to obtain ECoE from institute is between 1 to 2 weeks
STEP 4: UNDERTAKE MEDICALS AND PCC
Before lodgment of your application, you will need to undertake a medical examination by one of the panel doctors approved by the Australian Government. A list of the approved panel doctors can be found by visiting:http://www.immi.gov.au/contacts/overseas/i/india/panel-doctors.htm. Once you have undertaken the medical examination, your doctor will forward the medical reports and documents directly to the visa office.
STEP 5: APPLICATION LODGMENT
At this stage student is required to make a visa application to Department of Immigration and Border protection (DIBP), Australia. For that you will need to provide the documents outlined in the checklist of DIBP website i.e. https://www.homeaffairs.gov.au/Trav/Visa.
STEP 6: APPLICATION OUTCOME
After getting the outcome of your application from Department of Immigration and Border protection (DIBP) , Australia. we will assist you in remaining procedure.

